Introduction to the Federal Budget Process
Published on Jun 21, 2021 in Federal Advocacy
Each year, as the President and Congress work to craft the nation’s spending plan, your advocacy can influence the budget ultimately signed into law. Read on to learn more about the federal budget process and then take action. Now is a critical window of opportunity: the House Committee on Appropriations is holding markup hearings later this week while the Senate continues to negotiate topline spending levels.
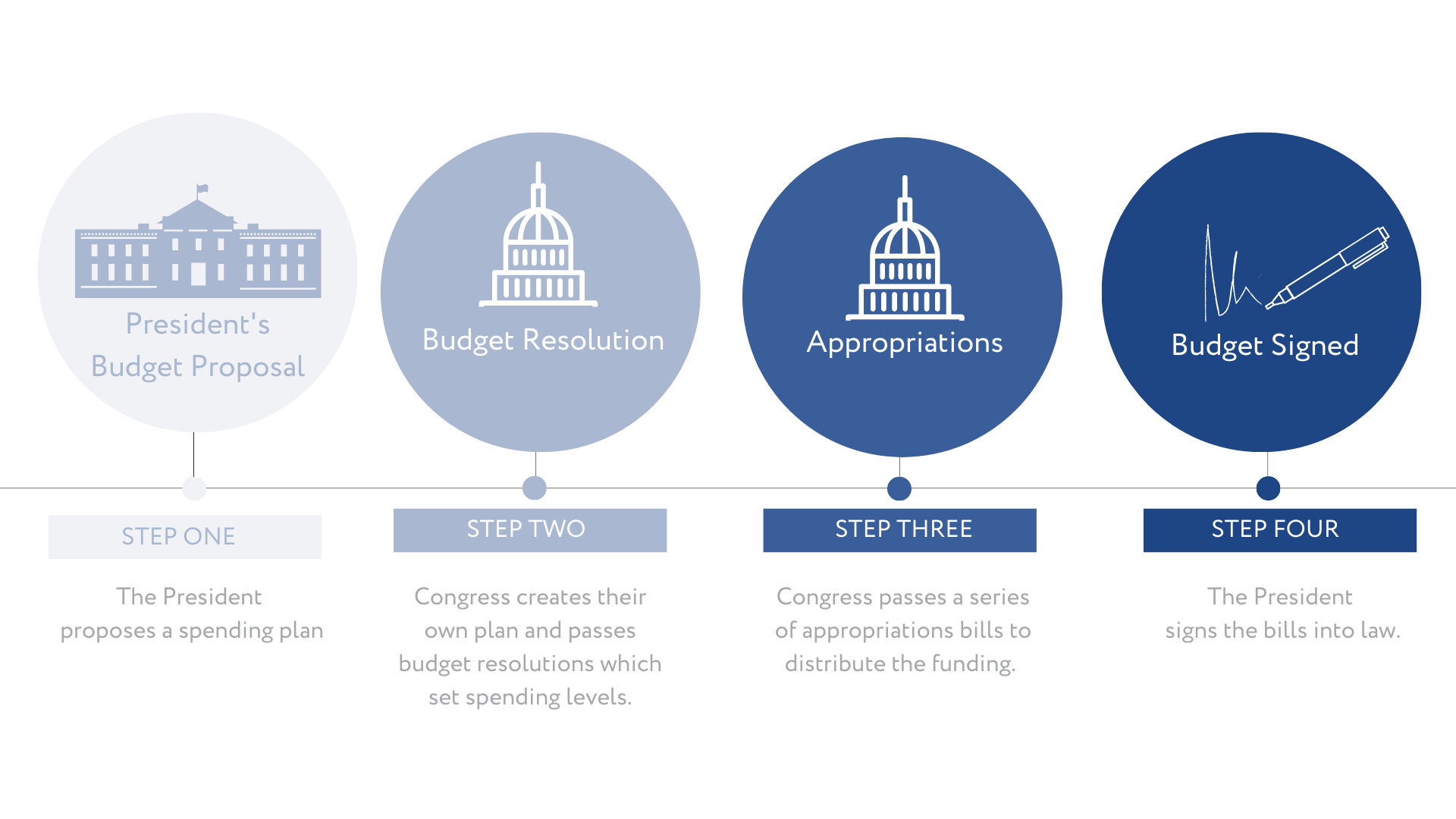
The Process:
Step One
Each year the President proposes a spending plan for the next federal fiscal year which outlines his spending priorities.
Step Two:
Based on the President’s budget proposal, House and Senate budget committees propose a budget resolution which establishes discretionary spending targets for the next fiscal year and identifies any policies that will need to move through budget reconciliation. The budget resolution then moves to the full floor for a vote and any differences are resolved in a conference committee. If they can't find agreement before the October 1st deadline, Congress also has the option of passing a Continuing Resolution. The Continuing Resolution provides a short-term vehicle to hold current funding levels in place while negotiations continue.
Step Three:
Congress divides the discretionary budget resolution voted on by the House and Senate among appropriations subcommittees. The subcommittees hold hearings and markup a series of appropriations bills before bringing them to the full committee and eventually the floor of the House and Senate for a full vote. Any differences are resolved in a conference committee.
Step Four:
The President must sign the Fiscal Year 2022 spending bill into law by October 1st in order to avoid a federal government shutdown.


